Special Information About the Provinces of Nepal
Nepal’s federal structure, implemented in 2015, divides the country into seven provinces. Each province has its unique cultural, geographical, and economic characteristics that contribute to the nation’s diversity. This division not only brought governance closer to the people but also created opportunities for equitable development across the country. For aspiring civil servants preparing for the Loksewa exams, understanding the specifics of each province is essential. Here’s a detailed look into each province's special features, with a focus on what makes them stand out.
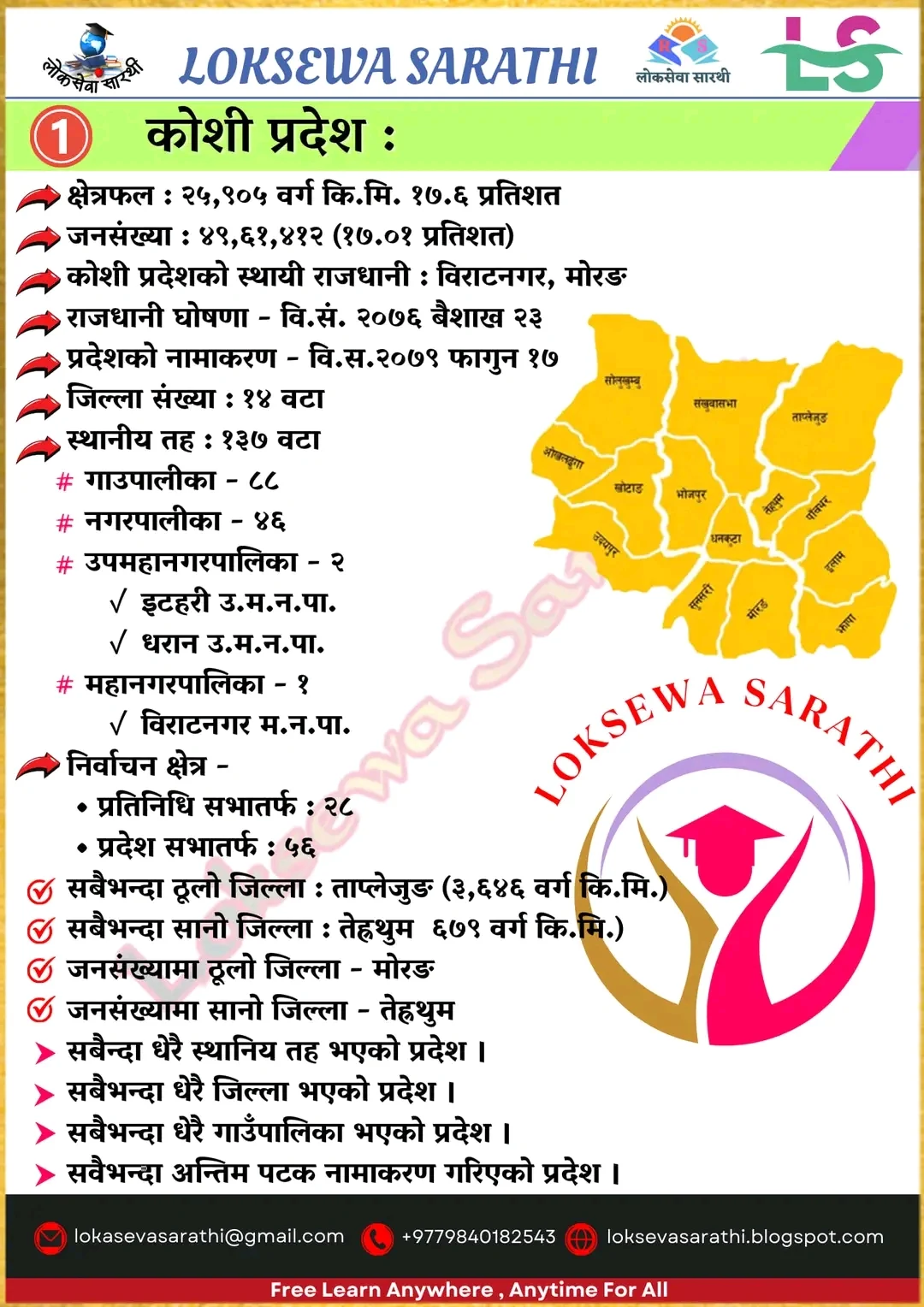
Koshi Province: A Mix of Nature and Industry
Headquarters:Biratnagar
Koshi Province is geographically diverse, stretching from the lowlands of the Terai to the heights of the Himalayas, including Mount Kanchenjunga. It is home to numerous ethnic communities, with a significant population of Kirant people, including Rais and Limbus. The province is an industrial hub, especially in the city of Biratnagar, contributing significantly to Nepal's economy.
Special Feature:
Presence of both industrial belts and Himalayan landscapes, making it a unique combination of economic and natural assets.
- Major Cities: Biratnagar (industrial hub), Dharan, and Dhankuta
- Key Attractions: Koshi Tappu Wildlife Reserve, Makalu Barun National Park, and Pathibhara Devi Temple
- Economy: Agriculture (tea, paddy, and jute), hydropower, and tourism
Madesh Province: The Agricultural Powerhouse
Headquarters: Janakpur
Madesh Province, located in the Terai region, is Nepal's most fertile area and a major agricultural zone. This province has a significant Madhesi population, contributing to a unique cultural and linguistic identity. It plays a vital role in food production for the nation.
Special Feature:
Madesh Province is the heartland of agriculture, producing essential crops like paddy, wheat, and sugarcane.
- Major Cities: Janakpur (famed for Janaki Temple), Birgunj (major trade hub), and Rajbiraj
- Key Attractions: Janaki Temple, Gadhimai Temple, and Parsa National Park
- Economy: Agriculture, trade, and cross-border commerce with India
Bagmati Province: The Economic and Cultural Center
Headquarters: Hetauda
Bagmati Province is the central province of Nepal, both geographically and economically. It includes the Kathmandu Valley, which houses the capital city, Kathmandu, and is the most developed region in the country. The province is rich in cultural heritage, with many UNESCO World Heritage Sites, and serves as the political, economic, and educational hub of Nepal.
Special Feature:
The concentration of national power, wealth, and cultural sites, including the Pashupatinath Temple and Swayambhunath Stupa.
- Major Cities: Kathmandu (capital of Nepal), Lalitpur, and Bhaktapur
- Key Attractions: Pashupatinath Temple, Swayambhunath Stupa, Boudhanath, and the ancient Durbar Squares
- Economy: Tourism, handicrafts, education, and financial services
Gandaki Province: The Tourism Hub
Headquarters: Pokhara
Gandaki Province is known for its picturesque landscapes, ranging from the Annapurna and Dhaulagiri ranges to the beautiful lakes of Pokhara. It is a major tourist destination, attracting both domestic and international travelers for trekking, paragliding, and other adventure activities.
Special Feature:
Tourism is the lifeblood of Gandaki Province, with Pokhara serving as the gateway to many trekking routes.
- Major Cities: Pokhara (tourism hub), Gorkha, and Baglung
- Key Attractions: Phewa Lake, Annapurna Base Camp, and Sarangkot
- Economy: Tourism, agriculture, and hydropower
Lumbini Province: The Spiritual Heart
Headquarters: Deukhuri
Lumbini Province is of immense religious significance, as it is the birthplace of Lord Buddha. Lumbini, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, attracts Buddhist pilgrims from around the world. The province also has fertile agricultural land in the Terai region and is a developing industrial area.
Special Feature:
Lumbini’s religious importance makes it a focal point for pilgrimage tourism and international cultural exchanges.
- Major Cities: Butwal (commercial center), Siddharthanagar (gateway to Lumbini), and Kapilvastu
- Key Attractions: Lumbini (Maya Devi Temple), Tilaurakot (ancient Kapilvastu), and Bardiya National Park
- Economy: Agriculture, tourism, and trade
Karnali Province: The Untouched Wilderness
Headquarters: Birendranagar
Karnali Province is Nepal’s largest but least populated and developed province. It is characterized by rugged terrain and remote villages, which have preserved their unique cultural practices. The province's untouched natural beauty, including Rara Lake and Shey Phoksundo National Park, makes it a hidden gem for eco-tourism.
Special Feature:
Karnali’s remoteness has preserved its pristine environment and traditional way of life, making it a focal point for sustainable development and eco-tourism.
- Major Cities: Birendranagar (Surkhet), Jumla, and Dolpa
- Key Attractions: Rara Lake, Shey Phoksundo National Park, and the Great Himalayan Trail
- Economy: Agriculture (barley, buckwheat), tourism, and medicinal herbs
Sudurpashchim Province: The Far-West Frontier
Headquarters: Godawari
Sudurpashchim Province, located in the far-western part of Nepal, has diverse geography ranging from the plains of Terai to the high mountains. The province has a unique blend of ethnic groups, including Tharus and Doteli communities, and retains strong traditional practices. It is also a developing region with great potential in agriculture, tourism, and hydropower.
Special Feature:
Sudurpashchim is known for its cultural diversity and untapped potential in hydropower and tourism, particularly around Shuklaphanta Wildlife Reserve and Khaptad National Park.
- Major Cities: Dhangadhi (economic hub), Mahendranagar, and Dadeldhura
- Key Attractions: Shuklaphanta Wildlife Reserve, Khaptad National Park, and the Seti River
- Economy: Agriculture, forestry, and remittance from abroad
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Loksewa Aspirants
Understanding the unique features of each province is crucial for Loksewa preparations. From industrial growth in Koshi Province to cultural and religious tourism in Lumbini Province, and from agricultural prominence in Madesh Province to sustainable development challenges in Karnali, each province presents its own opportunities and challenges. Loksewa aspirants should focus on regional policies, economic activities, and cultural characteristics when preparing for province-specific questions. Developing a strong grasp of these aspects will be key to success in the Loksewa exam and future public service roles in Nepal.
For more updates and detailed information on Nepal's provinces and other Loksewa-related topics, stay tuned to Loksewa Sarathi.
Alert
If your copyrighted material has been indexed by our site and if you want to remove then please Contact Us immediately, we will remove it within 3-4 days. We are sharing the Note/PDF which is already available on the internet only for educational purposes.